************* Snell_Huyg_lb.dwg ************* ************* Snell_Huyg_ub.dwg ************
Willebrord van Royen Snell (1580 - 1626),
who is today known for his discovery of the law of reflection and refraction, was a student of
Ludolph van Ceulen (1540 - 1610)
at the University of Leyden.
Ludolph took the same method Archimedes used almost 19 centuries ago, and computed the value of p up tp 35-th decimal place
using 262 -sided polygon ,inscribed and circumscribed.
Snell searched for better lower and upper bounds so that the value of p can be computed using less number of sides of polygon.
And he found the following sets. Although he could not prove the proposition (which was later done by
Christiaan Huygens (1629 - 1695))
, he used this result to verify Ludolph's 35-th decimal place using only 230-sided polygon.


************* Snell_Huyg_lb.dwg *************
************* Snell_Huyg_ub.dwg ************
To create these drawings:
Load pi_approximation.lsp (load "pi_approximation")
Then from command line, type Snell_Huygens_LB for lower bound drawing.
And from command line, type Snell_Huygens_UB for upper bound drawing.
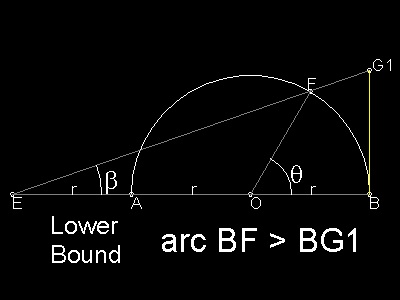
Referenced drawing: Snell_Huygens_lb.dwg
BG1 : representing the half the side-length of the circumscribing polygon
BG1 = 3r tan b (1)
In triangle EOF:
Sine law : EF/(sin(p-q) = r / sin b (2)
Cosine law: EF2 = EO2 = FO2 - 2EO.FO.cos (p-q)
=(2r)2 = r2 + 2.2r.r.cos(q)
=5 r2 + 4r2cos(q)
Therefore EF = r (5 + 4cos(q))1/2 (3)
Substituting (3) into (2),
sin b = sin q / (5 + 4cos(q))1/2 (4)
Using the equality cos b = 1 -sin2 b,
cos b = (cos q + 2)2 / (5 + 4 cos q)1/2
Then tan b = sin q / (2 + cos q)
Finally ,
BG1 = 3 r sin q /(2 + cos q)
|
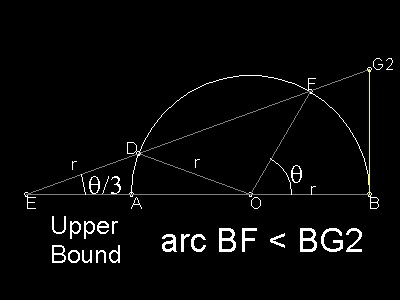
Referenced drawing: Snell_Huygens_ub.dwg Length ED is set equal to r. Note that angle DEA = q / 3, and this is exactly the same configuration Archimedes used for trisecting the given angle q. EO = 2r cos(q/3) BG2 = EB.tan(q/3) = (EO + r)tan(q/3) = r(2 cos(q/3) + 1) tan(q/3) |
What Snell found and later proved rigorously by Huygens is summarized as follows: BG1 < arc BF < BG2 or 3 r sin q /(2 + cos q) < r q < r(2 cos(q/3) + 1) tan(q/3) Starting with a hexagon , and after doubling the number of sides of ploygon k times (i.e. 2k times) ,this inequality can be written as follows: 6 x 2k x 3 sin a /(2 + cos a) < p < 6 x 2k(2 cos(a/3) + 1) tan(a/3) where, a = q / 2k = (p/6)/2k A simple program is run to check the efficency of these limits. Load the program "pi_approximation.lsp", and run typing Snell_pi in the command line window. The result are given below. ** k ** Lower bound : Upper bound error p - LB : UB - p ** 0 ** 3.14023 73433 66169 : 3.14174 00162 53954 error 0.00135531 : 0.000147363 ** 1 ** 3.14150 99936 42921 : 3.14160 17882 54884 error 8.26599e-005 : 9.13467e-006 ** 2 ** 3.14158 75188 57949 : 3.14159 32233 40417 error 5.13473e-006 : 5.69751e-007 ** 3 ** 3.14159 23331 59636 : 3.14159 26891 81042 error 3.2043e-007 : 3.55912e-008 ** 4 ** 3.14159 26335 70565 : 3.14159 26558 13962 error 2.00192e-008 : 2.22417e-009 ** 5 ** 3.14159 26523 38710 : 3.14159 26537 28799 error 1.25108e-009 : 1.39006e-010 ** 6 ** 3.14159 26535 11601 : 3.14159 26535 98480 error 7.81912e-011 : 8.68772e-012 ** 7 ** 3.14159 26535 84905 : 3.14159 26535 90335 error 4.8872e-012 : 5.42233e-013 ** 8 ** 3.14159 26535 89487 : 3.14159 26535 89826 error 3.05533e-013 : 3.37508e-014 ** 9 ** 3.14159 26535 89774 : 3.14159 26535 89794 error 1.86517e-014 : 1.77636e-015 The result for hexagon is better than Archimedes' 96-sided polygon case , and Snell's 96-sided case gives the correct number up to 6-th decimal place . He went further to verify his teacher's (Ludolph) work up to 35-th decimal place. |
Some of Huygens result to be added here. |
René Descartes
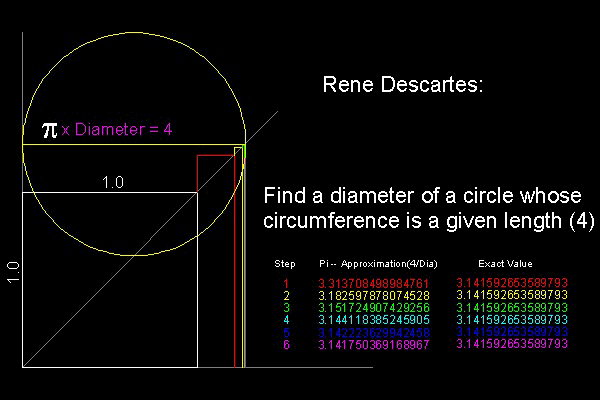
******************* Descartes_circle_square_desc.dwg *******************
For detail, go to the section René Descartes.
Kochansky published this result in 1685.
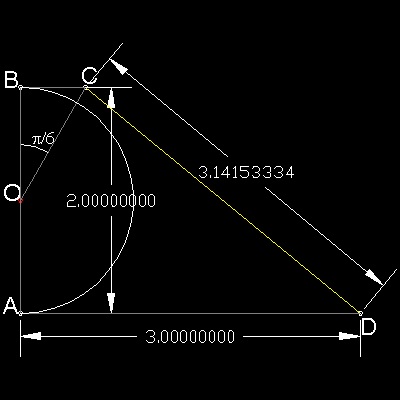
OA = OB = r, and AD = 3r
BC is paralllel to AD, and angle BOC = 30 degrees.
Then CD = 3.141533..
*************** Kochansky.dwg ***************
To create this drawing :
Load pi_construction.lsp (load "pi_construction")
Then from command line, type Kochansky
Jacob de Gelder (1765- 1848) published this result in 1849.
This is based on the approximation 355/113 = 3 + 42/(72 + 82).
This decimal portion is to be constructed.
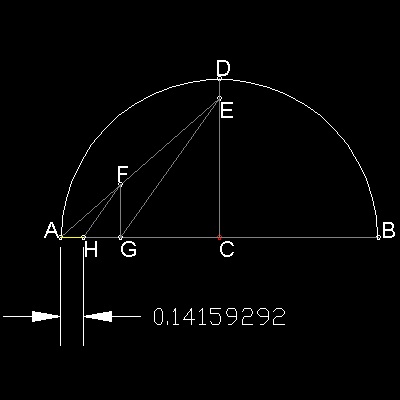
CD = 1, CE = 7/8, AF = 1/2
FG is parallel to CD, and HF is parallel to GE.
Then AH = 42/(72 + 82).
**************** Gelder.dwg *****************
To create this drawing :
Load pi_construction.lsp (load "pi_construction")
Then from command line, type Gelder
Hobson published this result in 1913. He constructed the approximate value of square root of pi,which is the true "circle squaring". p1/2 = 1.77245... His constructed length is 1.77246...,which is very,very close!!
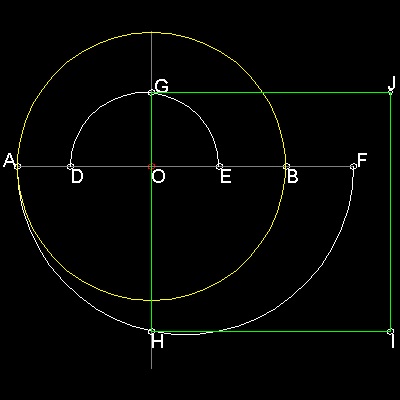
OA = 1.0, OD = 3/5, OF = 3/2, and OE = 1/2
Draw the semicircles DGE , AHF with DE and AF as diameters.
The perpendicular to AB through O intersects These semicircles at G & H.
Then GH = 1.77246...
**************** Hobson.dwg *****************
To create this drawing :
Load pi_construction.lsp (load "pi_construction")
Then from command line, type Hobson
All questions/suggestions should be sent to Takaya Iwamoto
Last Updated Feb 12, 2007
Copyright 2006 Takaya Iwamoto All rights reserved.